Content
Each industry has its own benchmarks for debt, but .5 is reasonable ratio. Knowing your debt-to-asset ratio can be particularly helpful when preparing financial projections, regardless of the type of accounting your business currently uses. Calculating your business’s debt-to-asset ratio can provide interested parties with the numbers they need to make a decision on investing in or loaning funds to your company. DTI is an important indicator of a person’s or a family’s debt level. Credit card issuers, loan companies, and car dealers can all use DTI to assess their risk of doing business with different people. A person with a high ratio is seen by lenders as someone that might not be able to repay what they owe.

Assets are items of monetary value used over time to produce a benefit for the asset’s holder. If the owners of Assets are a company, these assets are stated in the balance sheet for the accounting records. The debt ratio of a business is used in order to determine how much risk that company has acquired.
What Does Debt Ratio Mean in Finance?
From the result above, we can see that the utility company has taken the somewhat conservative approach of not using too much leverage to finance the assets. This can be concluded from the less than than 50% of the debt ratio. In this case, Sandra can be more rest assured investing in this company even if for some reasons the company may not do well. A steadily rising D/E ratio may make it harder for a company to obtain financing in the future.
The purpose of calculating the debt ratio of a company is to give investors an idea of the company’s financial situation. Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and, services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. While we strive to provide a wide range offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions.
How the Debt Ratio Varies by Industry
To get a clearer picture and facilitate comparisons, analysts and investors will often modify the D/E ratio. They also assess the D/E ratio in the context of short-term leverage ratios, profitability, and growth expectations. So, now that you know how to calculate, interpret, and use the total debt-to-equity ratio, you may be wondering when to use it. Again, the debt-to-capital ratio can help you determine if you have too much business debt. Well, that depends on your business and the services or goods you offer. Now, look what happens if you increase your total debt by taking out a $10,000 business loan.
- With this information, investors can leverage historical data to make more informed investment decisions on where they think the company’s financial health may go.
- This produces a number that tells you the proportion of your business’ assets that are financed by debt.
- The purpose of calculating the debt ratio of a company is to give investors an idea of the company’s financial situation.
- The ratio does this by calculating the proportion of the company’s debts as part of the company’s total assets.
- A high operating leverage ratio illustrates that a company is generating few sales, yet has high costs or margins that need to be covered.
- We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and, services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site.
These balance sheet categories may include items that would not normally be considered debt or equity in the traditional sense of a loan or an asset. Because the ratio can be distorted by retained earnings or losses, intangible assets, and pension plan adjustments, further research is usually needed to understand to what extent a company relies on debt. The higher the debt ratio, the more leveraged a company is, implying greater financial risk. At the same time, leverage is an important tool that companies use to grow, and many businesses find sustainable uses for debt.
Is there any other context you can provide?
As noted above, a company’s debt ratio is a measure of the extent of its financial leverage. Capital-intensive businesses, such as utilities and pipelines tend to have much higher debt ratios than others like the technology sector. The debt-to-equity ratio calculates if your debt is too much for your company. Investors, stakeholders, lenders, and creditors may look at your debt-to-equity ratio to determine if your business is a high or low risk. The higher the risk, the less likely you are to receive loans or have an investor come on board (which we’ll get into more later).
There are different types of DTI ratios, some of which are explained in detail below. Therefore, comparing a company’s debt to its total assets is akin to comparing the company’s debt balance to its funding sources, i.e. liabilities and equity. The fundamental accounting equation states that at all times, a company’s assets must equal the sum of its liabilities and equity. Leverage ratios represent the extent to which a business is utilizing borrowed money. Having high leverage in a firm’s capital structure can be risky, but it also provides benefits. Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is all your monthly debt payments divided by your gross monthly income.
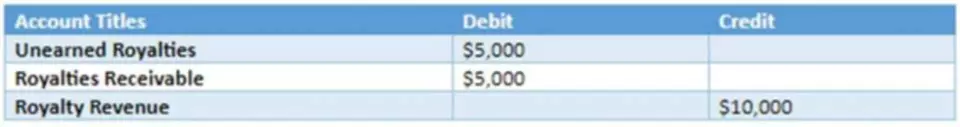
You do not need to share alimony, child support, or separate maintenance income unless you want it considered when calculating your result. If you receive income that is nontaxable, it may be upwardly adjusted to account for the nontaxable debt ratio formula status. The debt ratio is the ratio of a company’s debts to its assets, arrived at by dividing the sum of all its liabilities by the sum of all its assets. Simply multiply the result of the equation by 100% to make it a percentage.
The Ascent is a Motley Fool service that rates and reviews essential products for your everyday money matters. Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 https://www.bookstime.com/ years. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.
What other metrics should an investor take into account?
Perhaps 53.6% isn’t so bad after all when you consider that the industry average was about 75%. The result is that Starbucks has an easy time borrowing money—creditors trust that it is in a solid financial position and can be expected to pay them back in full. Add all of your liabilities together to get your total business debt. If you’re ready to learn your company’s debt-to-asset ratio, here are a few steps to help you get started.
In most cases, this is considered a very risky sign, indicating that the company may be at risk of bankruptcy. In the consumer lending and mortgage business, two common debt ratios used to assess a borrower’s ability to repay a loan or mortgage are the gross debt service ratio and the total debt service ratio. It’s great to compare debt ratios across companies; however, capital intensity and debt needs vary widely across sectors. The financial health of a firm may not be accurately represented by comparing debt ratios across industries.
Use of the Debt Ratio Formula
The easiest way to determine your company’s debt ratio is to be diligent about keeping thorough records of your business finances. This means registering your expenses, staying on top of any loans taken out, and tracking assets and depreciation. A low level of risk is preferable, and is linked to a more independent business that does not need to rely heavily on borrowed funds, and is therefore more financially stable. These businesses will have a low debt ratio (below .5 or 50%), indicating that most of their assets are fully owned (financed through the firm’s own equity, not debt). The debt ratio takes into account both short-term and long-term assets by applying both in the calculation of the total assets when compared with total debt owed by the company.
- In this article, we’ll review the debt ratio and why it is an essential concept for students interested in corporate finance.
- You can use the debt ratio calculator below to quickly determine the leverage a company uses to supply its assets using debts by entering the required numbers.
- Lenders also check your past records and installment payments to ensure you actively repay your debts.
- This calculator is for educational purposes only and is not a denial or approval of credit.
- A debt ratio of 30% may be too high for an industry with volatile cash flows, in which most businesses take on little debt.
- In turn, if the majority of assets are owned by shareholders, the company is considered less leveraged and more financially stable.
- He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
Published By

Latest entries
 allPost2025.01.22Mittens the cat becomes accidental frequent flyer after being mistakenly left on a plane
allPost2025.01.22Mittens the cat becomes accidental frequent flyer after being mistakenly left on a plane allPost2025.01.22This Morning’s Top Headlines – Jan. 22 | Morning News NOW
allPost2025.01.22This Morning’s Top Headlines – Jan. 22 | Morning News NOW allPost2025.01.22Experience Premier Online Casino Gaming in English at Brango Casino – Available for New Zealand Players
allPost2025.01.22Experience Premier Online Casino Gaming in English at Brango Casino – Available for New Zealand Players allPost2025.01.22Spielen Sie in Casinia Casino: Das Online-Casino Erlebnis in Deutsch für Schweizer Spieler
allPost2025.01.22Spielen Sie in Casinia Casino: Das Online-Casino Erlebnis in Deutsch für Schweizer Spieler